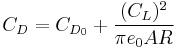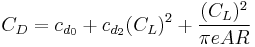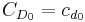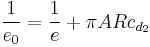Oswald efficiency number
The Oswald efficiency, similar to the span efficiency, is a correction factor that represents the change in drag with lift of a three dimensional wing or airplane, as compared with an ideal wing having the same aspect ratio and an elliptical lift distribution.[1]
Contents |
Definition
The Oswald efficiency is defined for the cases where the overall coefficient of drag of the wing or airplane has a constant+quadratic dependence on the aircraft lift coefficient
where
-
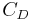
is the overall drag coefficient, 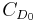
is the zero-lift drag coefficient, 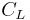
is the aircraft lift coefficient, 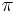
is the circumference-to-diameter ratio of a circle, 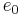
is the Oswald efficiency number 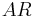
is the aspect ratio
For conventional fixed-wing aircraft with moderate aspect ratio and sweep, Oswald efficiency number with wing flaps retracted is typically between 0.7 and 0.85. At supersonic speeds, Oswald efficiency number decreases substantially. For example, at Mach 1.2 Oswald efficiency number is likely to be between 0.3 and 0.5.[1]
Comparison with span efficiency factor
It is frequently assumed that Oswald efficiency number is the same as the span efficiency factor which appears in Lifting-line theory, and in fact the same symbol e is typically used for both. But this assumes that the profile drag coefficient is independent of 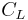 , which is certainly not true in general. Assuming that the profile drag itself has a constant+quadratic dependence on
, which is certainly not true in general. Assuming that the profile drag itself has a constant+quadratic dependence on 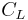 , an alternative drag coefficient breakdown can be given by
, an alternative drag coefficient breakdown can be given by
where
-
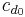
is the constant part of the profile drag coefficient, 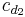
is the quadratic part of the profile drag coefficient, 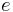
is the wing span efficiency factor from inviscid theory, such as Lifting-line theory
Equating the two 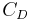 expressions gives the relation between the Oswald efficiency number e0 and the lifting-line span efficiency e.
expressions gives the relation between the Oswald efficiency number e0 and the lifting-line span efficiency e.
For the typical situation 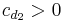 , we have
, we have  .
.
See also
Notes
References
- Raymer, Daniel P. (2006). Aircraft Design: A Conceptual Approach, Fourth edition. AIAA Education Series. ISBN 1-56347-829-3
- Anderson, John D. (2008). Introduction to Flight, Sixth edition. McGrawHill. ISBN 0-07-126318-7